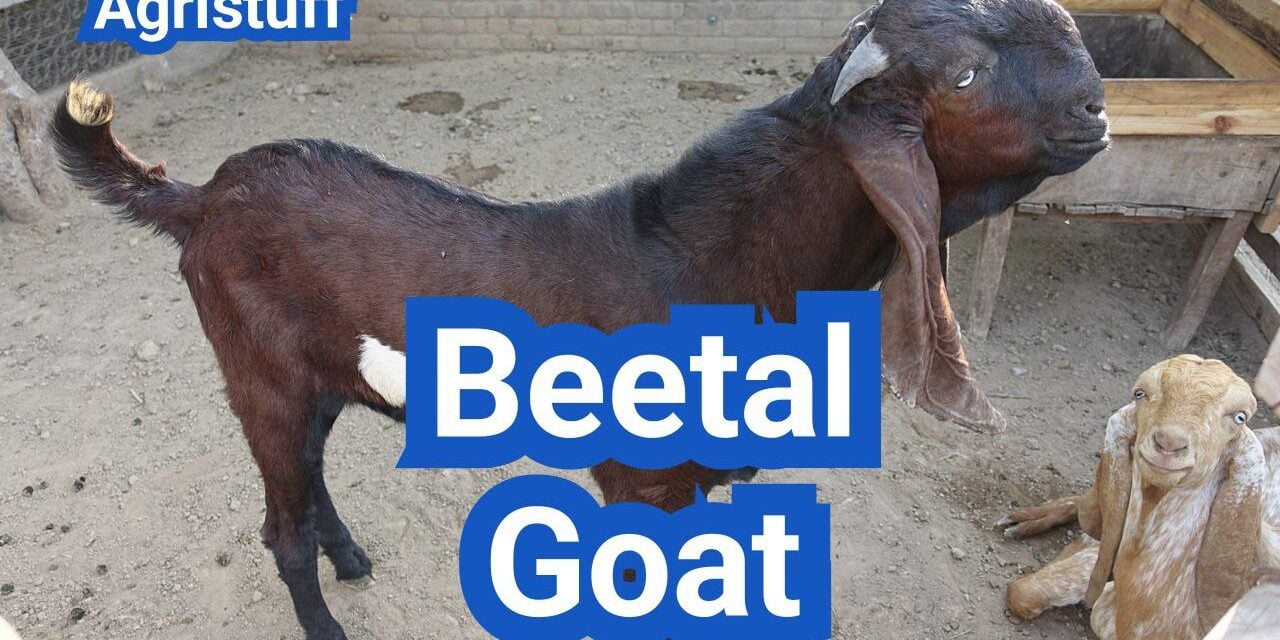
The Beetal breed is a significant livestock species originating from the Punjab region of India and Pakistan. Known for its large body size and high milk production, this breed has been a staple in the region for centuries.
Understanding the history and origin of this breed is crucial in appreciating its characteristics and uses. The Beetal breed has been used for both milk and meat production, making it a versatile and valuable asset to farmers.
This article will delve into the breed’s history, characteristics, breeding practices, and its various uses, providing a comprehensive overview of this important livestock species.
Key Takeaways
- Origin of the Beetal breed in the Punjab region
- Characteristics of the breed, including its large body size
- Uses of the breed for milk and meat production
- Importance of understanding the breed’s history and origin
- Breeding practices and their significance
The Origin and History of Beetal Goats
With roots in the Gurdaspur district, the Beetal goat’s history is deeply intertwined with local culture. The breed originated from the Batala area in the Punjab region, a fact that underscores its historical significance.
Historical Development of the Breed
The Beetal goat has a rich historical background that is closely linked to the agricultural practices of the Punjab region. Over time, the breed has been developed and refined through selective breeding practices, enhancing its desirable traits.
Key historical factors that influenced the development of the Beetal goat include:
- Geographic isolation in the Punjab region
- Selective breeding for desirable traits
- Cultural significance in local agricultural practices
Geographic Distribution in Pakistan and India
The Beetal goat is primarily found in the Punjab region, which spans across Pakistan and India. Its distribution is largely influenced by the breed’s adaptability to the local climate and agricultural practices.
In Pakistan, the Beetal goat is widely distributed in the Punjab province, where it is valued for its milk and meat production capabilities.
In India, the breed is found in the states of Punjab and Haryana, where it is recognized for its high-quality milk and meat.
Cultural Significance in Punjab Region
The Beetal goat holds significant cultural value in the Punjab region, where it is often associated with traditional farming practices and cultural festivities.
The breed is considered an integral part of the region’s agricultural heritage, with its rearing being passed down through generations.
Cultural practices that involve the Beetal goat include:
- Traditional farming practices
- Cultural festivals and celebrations
- Local cuisine that utilizes goat milk and meat
Understanding the Beetal Goat Breed

Beetal goats are renowned for their multipurpose utility in milk, meat, and hide production. This breed has been a cornerstone in various agricultural economies due to its versatility and productivity.
Classification and Recognition
The Beetal goat breed is classified as a multipurpose breed, utilized for its milk, meat, and hide. Its large body size and productivity have earned it recognition in the global goat industry.
Classification Summary:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Breed Type | Multipurpose |
| Primary Uses | Milk, Meat, Hide |
| Body Size | Large |
Population Status
The Beetal goat population is significant in regions where they are predominantly bred, such as Pakistan and India. Efforts to conserve and improve the breed are ongoing to ensure its sustainability.
Importance in Global Goat Industry
The Beetal goat breed plays a crucial role in the global goat industry due to its multipurpose utility and high productivity. It is valued for its milk production capabilities, meat quality, and hide production.
The breed’s importance is further underscored by its adaptability to various environments and its potential for crossbreeding programs aimed at improving goat productivity globally.
The significance of the Beetal goat breed in the global goat industry cannot be overstated, as it continues to be a vital component of agricultural economies.
Physical Characteristics of Beetal Goats
Beetal goats are characterized by their large size and distinctive physical features, setting them apart from other breeds. Their impressive stature and robust build make them a popular choice among farmers and breeders.
Size and Body Structure
Beetal goats are known for their substantial body size. Bucks typically weigh between 126-220 lbs, while does weigh between 77-132 lbs. Their body structure is sturdy, with a well-developed musculature that contributes to their overall size and strength.
The breed’s size is one of its most notable characteristics, making them suitable for various agricultural purposes. Their large body size is complemented by a short, lustrous coat that enhances their overall appearance.
Distinctive Features and Large Body Size
One of the distinctive features of Beetal goats is their long, hanging ears, which are not only aesthetically pleasing but also indicative of their breed. Their large body size, combined with these distinctive features, makes them easily recognizable.
- Large body size, with bucks weighing 126-220 lbs
- Does weighing between 77-132 lbs
- Short, lustrous coat
- Long, hanging ears
Color Variations
Beetal goats exhibit a variety of colors, adding to their visual appeal. While the primary color is often brown or black, they can also be found in other shades, including white and mixed patterns.
The color variations in Beetal goats are a result of their genetic diversity and breeding practices. This diversity in color adds to the breed’s attractiveness and uniqueness.
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is evident in Beetal goats, with bucks generally larger and more muscular than does. This difference is not only in size but also in the overall physical appearance, with bucks having a more pronounced musculature.
The sexual dimorphism in Beetal goats is a characteristic that is valued in breeding programs, as it allows for the selection of superior traits in both males and females.
Growth and Development

Understanding the growth stages of Beetal goats is essential for effective farm management. Beetal goats are known for their rapid growth and development, which makes them a valuable breed for farmers. Their growth pattern from birth to maturity involves several key stages that farmers need to be aware of to optimize their breeding and farming practices.
Birth Weight and Early Development
Beetal kids are born with a weight of around 3-4 kg (approximately 6-8.8 pounds), which is a crucial indicator of their health and future growth potential. Early development stages are vital as they set the foundation for the goat’s future productivity. Proper nutrition and healthcare during this period are essential for optimal growth.
Weight at 12 Months
By the time they reach 12 months, Beetal goats typically weigh around 21.8 kg (approximately 48 pounds). This significant weight gain is a testament to their rapid growth rate. Factors such as nutrition, genetics, and healthcare play a crucial role in achieving this weight.
Maturity Timeline
Beetal goats mature relatively quickly. Does are capable of breeding at around 17 months, indicating their reproductive maturity. This timeline is crucial for farmers to plan their breeding programs effectively.
Body Condition Scoring System
The body condition scoring system is a valuable tool used to assess the nutritional status and overall health of Beetal goats. It involves evaluating the fat reserves and muscle condition to determine if the goats are underweight, ideal, or overweight. This scoring system helps farmers make informed decisions about feeding and healthcare.
Beetal Goat Breeding Practices
Beetal goat breeding practices are crucial for the sustainability of this prolific breed. Effective breeding practices ensure the production of healthy kids and maximize the productivity of the herd.
Breeding Season and Estrus Cycle
The breeding season for Beetal goats typically occurs throughout the year, as they are non-seasonal breeders. However, the peak breeding season often aligns with the cooler months. Understanding the estrus cycle is vital for successful breeding. Beetal does exhibit a relatively short estrus cycle, typically ranging from 18 to 24 days.
Estrus Cycle Management: Farmers need to monitor the estrus cycle closely to determine the optimal breeding time. This involves observing behavioral changes in does, such as restlessness and vocalization, indicating they are in heat.
Buck Selection Criteria
Selecting the right buck is critical for improving the genetic quality of the herd. Key criteria for buck selection include:
- Genetic lineage and pedigree
- Physical characteristics, such as size and body structure
- Reproductive health and fertility
According to a study on Beetal goat breeding, “The selection of bucks with superior genetic traits significantly enhances the overall productivity of the herd”
Selection of genetically superior bucks is crucial for the improvement of Beetal goat herds, as it directly impacts the growth rate and fertility of offspring.
| Selection Criteria | Importance | Evaluation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Lineage | High | Pedigree analysis |
| Physical Characteristics | Medium | Visual inspection |
| Reproductive Health | High | Fertility testing |
Doe Management
Effective doe management is essential for successful kidding and overall herd health. This includes:
- Nutritional management to ensure optimal body condition
- Health checks to monitor for diseases and parasites
- Record-keeping to track reproductive history
Beetal does are prolific breeders, averaging 1.66 kids per litter. Proper management practices can further enhance this productivity.
Kidding Process and Management
The kidding process requires careful monitoring to ensure the health and safety of both the doe and kids. This involves:
- Preparing a clean and safe kidding environment
- Assisting during kidding if necessary
- Providing post-kidding care, including colostrum feeding to newborns
Proper kidding management is crucial for reducing mortality rates among newborn kids and ensuring the overall success of the breeding program.
Milk Production and Quality

Beetal goats are renowned for their milk production capabilities, making them a valuable asset in the dairy industry. Their milk is not only a source of nutrition but also contributes significantly to the livelihoods of many farmers.
Average Milk Yield Per Day
Beetal does are known to produce an average of 1.8 liters of milk per day. This yield is significant and places the Beetal breed among the prominent dairy goat breeds.
Milk Fat Content and Composition
The milk fat content of Beetal goats is around 5%, making their milk rich and suitable for various dairy products. The composition of the milk is also noteworthy for its nutritional value.
Lactation Period Duration
The lactation period for Beetal goats lasts approximately 161 days. This duration is crucial for dairy farmers as it influences the overall milk production and the frequency of kidding.
Factors Affecting Milk Production
Several factors affect the milk production of Beetal goats, including nutrition, health management, and breeding practices. Ensuring optimal conditions in these areas can significantly enhance milk yield and quality.
| Milk Production Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Average Milk Yield Per Day | 1.8 liters |
| Milk Fat Content | 5% |
| Lactation Period | 161 days |
Optimizing Milk Production: To maximize milk production, farmers should focus on providing a balanced diet, ensuring proper health care, and implementing effective breeding strategies. By doing so, the potential of Beetal goats in dairy production can be fully realized.
Meat Production Capabilities

The Beetal goat breed is a significant contributor to the global meat industry due to its impressive growth rate and meat quality. Beetal goats are known for their fast growth rate, which makes them highly suitable for meat production. This characteristic, combined with their high-quality meat, has made them a preferred choice among farmers and consumers alike.
Growth Rate for Meat
Beetal goats exhibit a rapid growth rate, which is a crucial factor in their meat production capabilities. They can achieve market weight quickly, typically within 6 to 12 months, depending on feeding and management practices.
- Average Daily Gain: Beetal goats can gain up to 150-200 grams per day under optimal conditions.
- Market Readiness: They are usually ready for market within a year, making them a lucrative option for farmers.
Meat Quality and Characteristics
The meat of Beetal goats is known for its tenderness and flavor, making it highly sought after. The quality of the meat is influenced by factors such as diet, age at slaughter, and breeding practices.
Meat Characteristics:
- Tender and flavorful
- Fine texture
- Good marbling, which enhances the taste
Dressing Percentage
The dressing percentage of Beetal goats is relatively high, indicating a good yield of saleable meat. The dressing percentage can vary based on factors like the animal’s condition and slaughter practices.
Typical Dressing Percentage: Beetal goats can have a dressing percentage ranging from 45% to 55%, which is considered good in the goat meat industry.
Market Value of Beetal Meat
The market value of Beetal goat meat is influenced by its quality, demand, and regional preferences. Generally, Beetal goat meat commands a premium price due to its desirable characteristics.
The demand for Beetal goat meat is significant in various regions, particularly where there is a cultural preference for goat meat. This demand drives the market value, making Beetal goats a valuable resource for the meat industry.
Other Uses of the Beetal Goat

The Beetal goat is a versatile breed with uses extending beyond milk and meat production. This breed offers a range of additional benefits, making it a valuable asset for farmers and communities.
Hide Production and Quality
Beetal goats are valued for their hides, which are used to produce high-quality leather. The hides are known for their durability and are often used in the production of leather goods such as shoes, belts, and handbags. The quality of Beetal goat hides is considered superior due to the breed’s large size and the thickness of their hides.
The process of preparing Beetal goat hides for leather production involves several stages, including curing, tanning, and finishing. The end product is a high-quality leather that is both durable and aesthetically pleasing.
Manure Value for Agriculture
Beetal goat manure is rich in nutrients and is highly valued for its use in agriculture. The manure is used as a natural fertilizer, improving soil fertility and structure. This organic fertilizer is particularly beneficial for crops that require high levels of nutrients.
The use of Beetal goat manure in agriculture not only enhances crop yields but also promotes sustainable farming practices by reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Cultural and Economic Importance
Beetal goats hold significant cultural and economic importance in the regions where they are bred. They are often used in traditional ceremonies and are considered a symbol of prosperity. Economically, Beetal goats contribute to the livelihoods of many farmers and their families through the sale of milk, meat, and other products.
The breed’s cultural significance is also reflected in its role in local economies, where it provides employment opportunities and generates income through various goat-related products and services.
Housing Requirements for Beetal Goats

Beetal goats require well-designed housing to protect them from extreme weather conditions. Proper housing is essential for their health, productivity, and overall well-being.
Shelter Design and Materials
The shelter design for Beetal goats should be sturdy, well-ventilated, and constructed from materials that provide adequate insulation against both heat and cold. Common materials used include brick, concrete, and wood, with roofing materials such as tiles or corrugated iron sheets.
Key considerations for shelter design include:
- Orientation to maximize natural ventilation and sunlight
- Adequate drainage to prevent waterlogging
- Protection from wind and rain
Space Requirements
Beetal goats need sufficient space to move comfortably. The recommended space per goat is approximately 1.5 to 2 square meters indoors and 3 to 4 square meters outdoors for exercise.
Environmental Adaptations
Environmental adaptations are crucial for maintaining the health of Beetal goats. This includes providing shade, ensuring good ventilation, and using bedding materials like straw or sand to keep the floor dry and comfortable.
“A well-designed housing system not only protects the goats from harsh weather but also enhances their productivity and welfare.” – Expert in Goat Farming
Fencing Needs and Options
Fencing is a critical aspect of Beetal goat housing, as it prevents escape and protects the goats from predators. Fencing options include wooden or metal fencing, with a recommended height of at least 1.5 meters.
Fencing considerations:
- Durability and strength
- Visibility to prevent accidental injury
- Cost-effectiveness
By carefully planning and implementing housing that meets these requirements, farmers can significantly improve the health and productivity of their Beetal goats.
Feeding and Nutrition Management
Effective feeding and nutrition management are crucial for the health and productivity of Beetal goats. A well-balanced diet supports their growth, milk production, and overall well-being.
Basic Dietary Requirements
Beetal goats are adaptable to various feeding regimes but require a diet rich in nutrients. Their basic dietary needs include good-quality hay, fresh forage, and clean water. The nutritional requirements vary based on factors such as age, sex, and production level.
Nutritional Components:
- Crude Protein: Essential for growth and milk production
- Energy: Required for maintenance and productivity
- Minerals and Vitamins: Crucial for overall health
Feeding Schedule and Amounts
A consistent feeding schedule is vital to maintain the health of Beetal goats. The amount of feed depends on the goat’s age, size, and production status.
| Age | Feed Type | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 0-3 months | Milk/Colostrum | 1-2 liters/day |
| 3-6 months | Starter Feed | 0.5-1 kg/day |
| Adult | Hay and Grains | 1-2 kg/day |
Supplementation Needs
Supplementation is necessary to ensure Beetal goats receive all required nutrients. Common supplements include minerals and vitamins, which can be added to their feed or provided separately.
Water Requirements and Quality
Access to clean, fresh water is essential for Beetal goats. Water quality significantly impacts their health, and regular checks are necessary to ensure water purity.
Key Considerations:
- Ensure water is free from contaminants
- Provide adequate water quantity based on the number of goats
- Regularly clean water containers
Health Management and Common Issues

Maintaining optimal health in Beetal goats involves a comprehensive approach including preventative care, disease management, and parasite control. Effective health management is crucial for ensuring the productivity and longevity of these animals.
Preventative Care Protocols
Preventative care is the cornerstone of maintaining healthy Beetal goats. This includes regular health checks, maintaining a clean living environment, and providing vaccinations. Regular monitoring helps in early detection of diseases, allowing for timely intervention.
Common Diseases and Treatments
Beetal goats are susceptible to various diseases, including parasitic infections, respiratory diseases, and reproductive issues. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent the spread of disease and reduce mortality rates. Common treatments include antiparasitics, antibiotics, and supportive care.
Parasite Control Methods
Parasite control is critical in Beetal goat health management. Effective methods include rotational grazing, strategic deworming, and the use of parasite-resistant breeding stock. Monitoring parasite loads regularly helps in determining the need for deworming.
Vaccination Schedule
A well-planned vaccination schedule is vital for protecting Beetal goats against infectious diseases. Vaccinations should be administered according to a schedule that considers the age, health status, and risk factors of the animals. Consulting with a veterinarian is recommended to develop an appropriate vaccination program.
By implementing these health management strategies, Beetal goat farmers can significantly improve the health and productivity of their animals, leading to better economic outcomes.
Beetal Goat Crossbreeding Programs

By crossing Beetal goats with breeds like Saanen and Alpine, farmers can achieve significant improvements in milk yield and quality. Beetal goat crossbreeding programs have been designed to leverage the strengths of different breeds, resulting in improved productivity and hardiness.
Saanen × Beetal Crosses
The Saanen breed, known for its high milk production, has been crossed with Beetal goats to create a hybrid that combines the milk yield of Saanen with the hardiness of Beetal. This crossbreeding has shown promising results in terms of increased milk production while maintaining the adaptability of Beetal goats.
Alpine × Beetal Crosses
Alpine × Beetal crosses aim to combine the robust milk production capabilities of Alpine goats with the desirable traits of Beetal goats. This cross has resulted in goats that are not only productive but also resilient to various environmental conditions.
Benefits of Crossbreeding
Crossbreeding Beetal goats with other breeds offers several benefits, including:
- Improved milk and meat production
- Enhanced hardiness and adaptability
- Better resistance to diseases
- Increased productivity
The overall effect is a more robust and productive goat population that can thrive in various farming conditions.
Performance of Crossbred Animals
The performance of crossbred animals has been a key area of focus in Beetal goat crossbreeding programs. Studies have shown that crossbred goats exhibit superior growth rates, improved milk yield, and better overall health compared to purebred Beetal goats.
Monitoring the performance of these crossbred animals is crucial to understanding the long-term benefits and challenges of crossbreeding programs.
Comparison: Beetal Goat vs. Jamunapari Goat

When it comes to comparing goat breeds, the Beetal and Jamunapari goats are two prominent breeds in the Indian subcontinent. Both breeds have their unique characteristics and are valued for different purposes.
Physical Differences
One of the primary distinctions between Beetal and Jamunapari goats lies in their physical attributes. Beetal goats are generally larger in size compared to Jamunapari goats. Beetal goats have a more robust body structure, which makes them suitable for meat production. In contrast, Jamunapari goats, while also used for meat, are known for their distinctive long ears and Roman nose.
Production Capabilities
In terms of production capabilities, Beetal goats are renowned for their higher milk yield compared to Jamunapari goats. Beetal goats can produce significantly more milk, making them a preferred choice for dairy farming. On the other hand, Jamunapari goats are also valued for their milk, although their production is not as high as that of Beetal goats.
Adaptability Comparison
Both breeds have shown adaptability to various environmental conditions. However, Beetal goats are known to be more adaptable to harsh conditions, making them suitable for farming in diverse regions. Jamunapari goats also exhibit adaptability but are more commonly found in specific regions.
Economic Value Differences
The economic value of Beetal and Jamunapari goats differs based on their production capabilities and market demand. Beetal goats, due to their higher milk production and larger body size, often command a higher price in the market. Jamunapari goats, while valuable, are priced differently based on their specific characteristics and the purpose they serve.
Economic Considerations and Market Value
Understanding the economic aspects of Beetal goat farming is crucial for its success. The breed offers significant potential for farmers due to its milk and meat production capabilities. As such, analyzing the economic considerations and market value of Beetal goats is essential for making informed decisions.
Beetal Goat Price Ranges
The price of Beetal goats can vary significantly based on factors such as age, sex, and breed quality. Generally, younger goats are less expensive than mature ones, and females are often priced differently than males due to their milk production potential.
Price Range for Beetal Goats:
| Age | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| 0-3 months | $50-$150 |
| 6-12 months | $100-$300 |
| Mature (1-3 years) | $200-$500 |
Factors Affecting Pricing
Several factors influence the pricing of Beetal goats, including genetics, health status, and demand in the market. Goats with superior breeding lines or those that are well-cared for tend to command higher prices.
Return on Investment
The return on investment for Beetal goat farming can be substantial, given the dual benefits of milk and meat production. Farmers can expect a significant income from selling both dairy products and meat, making it a viable business opportunity.
Market Opportunities in Different Regions
Beetal goats have market potential in various regions, particularly where there is a demand for their milk and meat. Regions with a strong dairy or meat production industry can benefit from introducing Beetal goats into their farming systems.
By understanding the economic considerations and market value of Beetal goats, farmers and investors can make informed decisions about entering or expanding their operations in Beetal goat farming.
At The End of: Beetal Goat
The Beetal goat is a significant breed known for its impressive milk and meat production capabilities, making it a valuable asset in various agricultural contexts. Throughout this article, we have explored the breed’s history, physical characteristics, breeding practices, and economic importance.
The Beetal goat’s adaptability and productivity have made it a popular choice among farmers, particularly in regions like Punjab. Its milk is rich in fat, and its meat is considered to be of high quality, contributing to its demand in local and international markets.
In conclusion, the Beetal goat is an important breed that plays a crucial role in the livestock industry. Its unique characteristics, combined with its economic significance, make it a breed worth understanding and promoting. As the demand for high-quality milk and meat continues to grow, the Beetal goat is poised to remain a vital component of agricultural production systems.
FAQ
What is the origin of the Beetal Goat breed?
The Beetal Goat breed originated in the Punjab region of Pakistan and India, where it has been raised for centuries for its milk, meat, and hide production.
What are the distinctive physical characteristics of Beetal Goats?
Beetal Goats are known for their large body size, with males weighing between 50-70 kg and females weighing between 30-50 kg. They have a sturdy build, long ears, and a variety of coat colors.
How much milk do Beetal Goats produce on average per day?
Beetal Goats are known for their high milk production, with an average yield of 2-3 liters per day. However, this can vary depending on factors such as nutrition, management, and genetics.
What is the breeding season for Beetal Goats?
Beetal Goats can breed throughout the year, but the breeding season typically peaks during the spring and fall months.
How are Beetal Goats used in agriculture?
Beetal Goats are used for milk, meat, and hide production. They are also used for manure production, which is valuable for agriculture.
What are the housing requirements for Beetal Goats?
Beetal Goats require shelter that protects them from extreme weather conditions, such as heat, cold, and rain. The shelter should be well-ventilated, dry, and provide adequate space for the goats to move around.
What are the dietary requirements for Beetal Goats?
Beetal Goats are ruminants and require a diet rich in fiber, including hay, grass, and other vegetation. They also require access to clean water and mineral supplements.
How are Beetal Goats crossed with other breeds?
Beetal Goats can be crossed with other breeds, such as Saanen and Alpine, to improve their milk production and other characteristics. The resulting crossbred animals can have improved productivity and hardiness.
How do Beetal Goats compare to Jamunapari Goats?
Beetal Goats are generally larger and more productive than Jamunapari Goats, with higher milk production and faster growth rates. However, Jamunapari Goats are known for their hardiness and adaptability.
What is the economic value of Beetal Goats?
Beetal Goats have significant economic value due to their milk, meat, and hide production. They are also used for manure production, which is valuable for agriculture.
What are the common health issues in Beetal Goats?
Beetal Goats are susceptible to various health issues, including parasites, diseases, and reproductive problems. Regular veterinary care and preventative measures can help mitigate these issues.
How can I care for Beetal Goats?
To care for Beetal Goats, provide them with adequate nutrition, shelter, and health care. Regular veterinary check-ups, proper feeding, and a clean living environment are essential for maintaining their health and productivity.
Conclusion of: Beetal Goat
Introduction: Why the Beetal Goat matters for today’s farmers
The Beetal Goat is a large, dual-purpose goat breed that originated in the Punjab region of India and Pakistan and is now attracting interest from smallholders and commercial farmers around the world. For producers who want one breed that can provide both milk and meat, the Beetal Goat offers an appealing balance of size, productivity, and adaptability.
Its long, pendulous ears, distinctive Roman nose, and strong frame make the Beetal Goat easy to recognize, while its capacity for good milk yield and fast-growing kids makes it valuable in practical farm systems. For U.S. farmers exploring new genetics or niche ethnic markets, understanding the Beetal Goat is an important step in planning a profitable and resilient goat enterprise. Oklahoma State University breeds of livestock resource
History and origin of the Beetal Goat
The Beetal Goat developed in the fertile plains of Punjab, a cross-border region that today lies between northern India and eastern Pakistan. Historically, small farmers selected Beetal Goat animals for their ability to thrive in a hot climate, walk long distances in search of forage, and still provide ample milk and meat.
Over generations, this selection pressure created a Beetal Goat type that resembles the famous Jamunapari breed in body shape but is somewhat smaller and often more prolific. In village systems the Beetal Goat was traditionally grazed on community land, fed crop residues, and integrated into mixed crop–livestock rotations, which helped families diversify their income and nutrition. FAO livestock and animal genetic resources information
Geographical distribution and current status of the Beetal Goat
Today, the Beetal Goat is still most common in Punjab districts of India and Pakistan, where it is recognized as an important indigenous breed. Government farms and research institutes in the region maintain Beetal Goat herds to conserve the genetic resource and to use it in crossbreeding with other dairy and meat breeds. Outside South Asia, the Beetal Goat is present mainly in small numbers or as part of crossbred populations, but interest is growing as farmers look for adaptable, dual-purpose goats.
For U.S. producers, pure Beetal Goat animals may be difficult to source, yet the breed’s characteristics are increasingly studied as a model for heat tolerance, good udder structure, and dual-purpose potential that could guide future breeding decisions. USDA overview of livestock and animal resources
Physical characteristics and appearance of the Beetal Goat
One reason the Beetal Goat stands out is its striking physical appearance. The Beetal Goat typically has a strong, deep body with a broad chest, long legs, and a slightly convex (Roman) nose profile. Coat color varies widely, including solid red, black, brown, and a range of pied or spotted patterns. The Beetal Goat usually has long, flat, pendulous ears that hang close to the head, giving the breed an elegant look.
Horns are often medium to long and may curve backward; in some management systems horns are disbudded for safety. Overall, the Beetal Goat shows a dairy-type frame combined with enough muscling to support meaningful meat production, making it visually similar to other dual-purpose goats that are already familiar to U.S. producers. Penn State Extension goat production information
Size, growth and bodyweight of the Beetal Goat
The Beetal Goat is considered a large breed by goat standards, especially when compared with many local village goats. Under good feeding and management, a mature Beetal Goat buck can reach substantial bodyweight and height, while mature does typically show strong frames and well-developed udders. Growth rates in Beetal Goat kids are influenced by genetics, colostrum intake, parasite control, and quality of feed, but the breed’s dual-purpose background allows young stock to reach market weights within a reasonable time frame when managed intensively.
For farmers in the United States, this means the Beetal Goat can be used to produce crossbred kids with improved growth potential, especially when matched with robust local or established meat goat lines that are already well adapted to U.S. conditions. Goats Extension national goat production resource
Milk production and lactation traits of the Beetal Goat
As a dairy type, the Beetal Goat is known for solid milk production relative to its body size, which is one of the reasons it has been favored in smallholder systems. A well-fed Beetal Goat doe can provide a meaningful amount of milk per lactation, supporting both home consumption and sale of surplus milk or value-added products such as cheese and yogurt. Lactation length, peak yield, and persistency in the Beetal Goat depend heavily on nutrition, health, breeding, and milking frequency.
In practice, Beetal Goat farmers aim for a steady flow of milk over many months rather than short, extremely high-yield bursts, which can be hard on the doe’s body. This moderate but reliable style of production can make the Beetal Goat a strong candidate for small- to medium-scale dairies that prioritize animal welfare and long productive lifespans. Langston University goat and small ruminant resources
Milk quality and product opportunities from Beetal Goat milk
Beyond volume, the Beetal Goat offers good milk composition that can work well for a variety of dairy products. Like many dairy-oriented breeds, Beetal Goat milk generally contains enough fat and protein to produce cheese, paneer, yogurt, ice cream, and other high-value items. Small-scale dairies and farmstead creameries are particularly interested in breeds like the Beetal Goat because higher solids can translate into better cheese yield per gallon of milk, which directly influences profitability.
In the United States, where consumer interest in ethnic and specialty cheeses is rising, Beetal Goat genetics may help dairies target niche markets that appreciate rich goat milk and products that reflect South Asian culinary traditions. U.S. FDA dairy and milk safety information
Meat production potential of the Beetal Goat
The Beetal Goat is not only a dairy animal; it also contributes significantly to meat production. Surplus male kids and cull does from Beetal Goat herds can be finished for meat, and their relatively large frames support good carcass weights and dressing percentages when managed properly. In many traditional markets, Beetal Goat meat is favored for its flavor and tenderness, and the breed’s size makes it suitable for both household consumption and commercial sale.
For U.S. producers, Beetal Goat genetics may be particularly interesting in areas with strong ethnic demand for goat meat, where customers appreciate larger carcasses and may even recognize the breed by name. Strategic crossbreeding of Beetal Goat does with established meat-type bucks can further improve growth rates and muscling while preserving the maternal and milk traits that underpin kid performance. USDA goat and meat goat information
Adaptation, climate tolerance and behavior of the Beetal Goat
The Beetal Goat evolved under hot, seasonally humid conditions, and this background gives the breed a useful level of heat tolerance when compared with some temperate-origin dairy goats. With proper shade, ventilation, and access to clean water, the Beetal Goat can handle high temperatures and still maintain reasonable productivity. Behaviorally, the Beetal Goat is typically active and alert but can be docile when handled regularly, making it manageable even in family-based systems.
The breed is also known to make good use of mixed vegetation, browsing shrubs and trees in addition to grazing, which can benefit pasture health when stocking density and rotation are planned correctly. For farmers facing warmer summers or climate variability, the Beetal Goat offers a blueprint for building herds that are comfortable and productive in challenging conditions. USDA Climate Hubs agriculture resources
Breeding goals and selection criteria for Beetal Goat herds
Clear breeding goals are essential when working with the Beetal Goat. Farmers typically select Beetal Goat breeding stock for strong udder attachment, correct teat placement, solid feet and legs, and good body capacity. Fertility and mothering ability are equally important; the best Beetal Goat does kid regularly, raise healthy twins or even triplets, and return to good body condition before the next breeding season.
Bucks should demonstrate good growth, masculinity, sound structure, and a family history of productive, long-lived females. In many programs, Beetal Goat breeders also record basic performance data such as birth weights, weaning weights, and milk yield so that selection decisions are rooted in measurable results rather than appearance alone. Extension resources on goat breeding and reproduction
Reproduction, kidding and kid management in Beetal Goat flocks
Reproductive management for the Beetal Goat follows general goat principles, but careful attention to detail can significantly improve kid survival and overall herd performance. The Beetal Goat typically reaches puberty at a similar age to other medium-large breeds, and controlled breeding allows farmers to plan kidding seasons when weather and forage are favorable.
At kidding, prompt assistance is only needed if the Beetal Goat doe shows signs of distress or prolonged labor; otherwise, minimal intervention is preferred. Newborn Beetal Goat kids should receive adequate colostrum within the first few hours of life, be dried and kept warm, and be monitored for navel health and vigor. Good kid management in a Beetal Goat flock lays the foundation for future productivity, because early setbacks often reduce lifetime performance and profitability. Goat kidding and kid care guidance
Feeding and nutrition plans for the Beetal Goat
Feeding the Beetal Goat correctly is one of the most powerful tools a farmer has to unlock the breed’s full potential. Beetal Goat animals are ruminants and rely on forage—pasture, hay, and browse—as the foundation of their diets, but high-producing does and fast-growing kids also need carefully balanced concentrates in many systems.
Rations for Beetal Goat herds must provide enough energy, protein, fiber, minerals, and vitamins to support maintenance, growth, pregnancy, and lactation, with adjustments made for body condition score and stage of production. Clean water and free-choice minerals are essential, and any dietary changes should be introduced gradually to avoid digestive upsets. Using established goat nutrition guidelines and working with a nutritionist where possible can help producers keep Beetal Goat herds healthy, productive, and cost-efficient. Goat nutrition and feeding reference
Housing, space and welfare requirements for the Beetal Goat
Proper housing is another key component of a successful Beetal Goat operation. The Beetal Goat needs dry, well-drained shelter that protects it from wind, rain, and extreme sun, while still allowing good ventilation. Overcrowding can lead to stress, disease transmission, and aggressive behavior, so each Beetal Goat should have adequate lying, feeding, and walking space based on age and class of animal.
Bedding such as straw or wood shavings should be kept clean and replenished regularly to reduce mastitis risk in does and foot problems in all animals. Pens and fencing for Beetal Goat herds should be sturdy enough to withstand rubbing and climbing, and safe handling areas are essential for hoof trimming, health checks, and routine management. Investing in good housing design helps Beetal Goat farmers cut labor time, reduce vet costs, and improve overall welfare. Extension guidance on housing for sheep and goats
Health management and common diseases in Beetal Goat herds
The Beetal Goat is generally hardy, but like any breed it can suffer from diseases and parasites if management is weak. Common health challenges for Beetal Goat herds include internal parasites (especially in warm, humid regions), coccidiosis in young kids, foot problems in wet conditions, and clostridial diseases if vaccination schedules are not maintained.
Some farms also monitor for chronic conditions such as caprine arthritis encephalitis (CAE) and caseous lymphadenitis (CL), since these can reduce productivity and market value in Beetal Goat breeding stock. A proactive health plan for Beetal Goat flocks includes regular fecal monitoring, targeted deworming, vaccination, biosecurity measures for new arrivals, and close observation of appetite, behavior, and body condition. Working with a qualified veterinarian familiar with goats is the best way to design an effective health program for Beetal Goat enterprises. Merck Veterinary Manual online reference
Beetal Goat and U.S. regulatory considerations
Farmers who plan to raise the Beetal Goat in the United States must keep regulatory issues in mind, even if their herd begins with crossbred animals instead of imported purebreds. All goats, including any Beetal Goat or Beetal-cross animals, are subject to identification and movement rules that vary by state but are anchored in national disease control programs such as scrapie eradication.
Producers who sell milk or processed dairy products from Beetal Goat herds must meet state and federal dairy regulations, and meat marketing must comply with inspection and labeling rules. Before investing heavily in Beetal Goat genetics, it is wise to check requirements with state departments of agriculture, cooperative extension, and local inspectors so that facility design, record keeping, and marketing plans meet legal standards from the start. USDA APHIS animal health and regulations portal
Marketing, economics and profitability of Beetal Goat enterprises
From an economic perspective, the Beetal Goat offers several revenue streams that can support profitability when managed carefully. A Beetal Goat herd can generate income from liquid milk, cheese and other dairy products, live breeding stock, meat from surplus kids and cull animals, and even value-added items like manure compost or agritourism experiences.
Profit depends on controlling feed, health, and labor costs while securing strong, reliable markets that appreciate the unique qualities of Beetal Goat products. In the U.S. context, ethnic communities often have high demand for goat meat and specialty dairy items, which can provide attractive prices if producers maintain quality and consistency. Careful record keeping, regular financial analysis, and close communication with buyers help Beetal Goat farmers refine their business models over time. Iowa State Extension small-farm goat production economics
Practical tips for beginners starting with Beetal Goat
For beginners, starting with the Beetal Goat should be a thoughtful, step-by-step process rather than a rushed purchase of animals. The first priority is education: new producers should study basic goat husbandry, health, and nutrition so they understand what the Beetal Goat needs to thrive. Visiting established farms, attending workshops, and speaking with veterinarians or extension agents can fill in many practical details before the first Beetal Goat is ever bought.
When it is time to purchase animals, beginners should focus on small numbers of high-quality Beetal Goat or Beetal-cross animals from reputable breeders with good health records. Starting small allows new farmers to learn systems, fencing, and marketing with lower risk, then expand as their skills, infrastructure, and customer base grow. Getting started in the goat business guide
Final thought
In summary, the Beetal Goat is a versatile, dual-purpose breed that can contribute meaningful milk and meat in a wide range of production systems. Its history in the Punjab region, strong frame, good udder traits, and ability to handle heat make the Beetal Goat especially interesting for farmers facing climate challenges or serving markets that value goat products. While pure Beetal Goat genetics may be harder to access in some countries, the breed’s characteristics can still guide crossbreeding and management strategies aimed at resilient, profitable herds. By combining sound husbandry, clear breeding goals, and careful attention to regulations and markets, producers can turn the Beetal Goat into a cornerstone of sustainable livestock operations. OSU goat breeds overview for further reading
Sources & References
When researching the Beetal Goat and building a management plan, producers should rely on authoritative, science-based resources from universities, government agencies, and recognized international organizations. The following websites provide high-quality information on goats, dairy and meat production, animal health, and regulatory frameworks that can be applied to Beetal Goat herds and crossbred operations. USDA, extension and veterinary references for goats
- Oklahoma State University Breeds of Livestock – goat breeds profiles
- USDA and USDA APHIS – animal health, identification and movement rules
- Cooperative Extension services – goat production, housing, nutrition and marketing
- Langston University – goat research and extension publications
- FAO – global livestock and animal genetic resources information
- Merck Veterinary Manual – goat diseases and veterinary reference